In the ever-evolving landscape of audio technology, wireless microphone systems have become indispensable tools for professionals and enthusiasts alike. This article aims to demystify the intricate workings of these systems, shedding light on the underlying technology that enables seamless and cable-free audio transmission.
Discover expert insights and recommendations on the best wireless microphone systems at SoundMaximum, ensuring you make an informed choice for your audio needs.
Basics of Sound Transmission
To grasp the core of wireless microphone systems, it is essential to initially grasp the basics of sound transmission. While wired microphones are dependable, they come with restrictions on mobility and flexibility. The shift to wireless technology stemmed from a demand for increased freedom of movement without sacrificing audio fidelity. The evolution towards wireless solutions was motivated by a necessity to enhance maneuverability while preserving the integrity of audio signals. This transition addresses the inherent limitations of traditional wired setups, ushering in a new era where users can experience untethered mobility without compromising the quality of their audio transmissions.
Components of a Wireless Microphone System
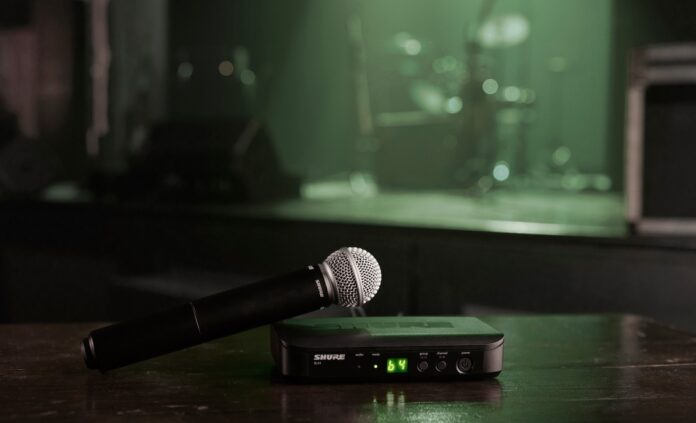
In the realm of wireless microphone systems, there are two essential elements working harmoniously to enable fluid audio transmission: the microphone transmitter and the receiver. These components play a critical role in guaranteeing that users enjoy the advantages of unrestricted mobility without any compromise in audio excellence. The synergy between the microphone transmitter and receiver is pivotal, allowing for a seamless transition into a cable-free environment. This dynamic duo ensures that the user not only embraces the freedom of movement but does so without sacrificing the pristine quality of the transmitted audio signals.

Microphone Transmitter
At the heart of every wireless microphone system is the microphone transmitter. This device serves as the source of the audio signal, capturing sound waves through the microphone element. The transmitter then converts these analog signals into radiofrequency (RF) waves for wireless transmission. Understanding the nuances of different types of microphones used in wireless systems is crucial, as they impact the overall performance and characteristics of the audio signal. Whether it’s a dynamic, condenser, or lavalier microphone, the choice depends on the specific application and user preferences.
Furthermore, the transmitter plays a critical role in determining the range and stability of the wireless connection. High-quality transmitters incorporate advanced technologies to mitigate interference, ensuring a clean and reliable signal. The importance of signal quality cannot be overstated, particularly in professional settings where audio clarity is paramount.
Receiver
On the receiving end, the wireless microphone system features a receiver that captures and processes the transmitted signals. Receivers are available in various configurations, including single-channel and multi-channel setups. A single-channel receiver is suitable for basic applications, while multi-channel receivers cater to more complex scenarios, allowing multiple microphones to operate simultaneously without interference.
Antennas are integral components of the receiver, enhancing its ability to capture signals effectively. Proper antenna positioning and orientation contribute to signal strength and overall system performance. Users can choose between internal and external antennas based on their specific needs and operational environments.
Understanding the synergy between the microphone transmitter and receiver is fundamental to optimizing the performance of a wireless microphone system. The delicate dance of converting, transmitting, and receiving signals wirelessly is what empowers users with the freedom to move while ensuring a reliable and high-quality audio experience. As we delve deeper into the intricacies of these components, we gain a more profound appreciation for the sophisticated technology that underlies the seemingly effortless magic of wireless microphone systems.

Signal Processing and Modulation
Analog and digital systems each have their strengths and weaknesses. This section discusses the advantages and disadvantages of both, with a focus on the benefits of digital signal processing in wireless microphone systems and the impact of modulation on signal quality and reliability. As wireless communication becomes more prevalent, ensuring secure transmissions is paramount. The article touches upon the role of encryption in wireless microphone systems and the importance of secure communication, especially in professional settings.
Batteries and Power Management
Within this segment, we delve into the diverse array of batteries employed in wireless microphone systems, examining factors like power consumption and offering pragmatic suggestions to enhance battery longevity. This becomes especially pivotal for prolonged usage, emphasizing the significance of managing power resources effectively. The discussion encompasses insights into various battery types, considerations related to power usage, and hands-on recommendations, collectively forming a comprehensive guide to ensure sustained and efficient performance during extended operational periods.

Best Practices for Using Wireless Microphone Systems
Ensuring peak performance necessitates the correct configuration and placement of both transmitters and receivers. This segment provides valuable perspectives on the most effective methods to guarantee flawless audio transmission. Offering comprehensive guidance, the article addresses critical aspects such as monitoring signal strength, fine-tuning frequencies, and resolving prevalent issues that users might face with wireless microphone systems. By imparting insights into these best practices, the article empowers users to navigate the complexities of setup, optimize signal quality, and troubleshoot common challenges, fostering a seamless and trouble-free experience in their audio endeavors.
Troubleshooting Tips for Wireless Microphone Systems
Even the most advanced wireless microphone systems may encounter occasional challenges. Here are some common issues users might face and practical solutions to troubleshoot them:
Interference Issues:
- Problem: Signal interference causing dropouts or static.
- Solution:
- Check for other electronic devices operating on similar frequencies.
- Reposition the receiver or transmitter to minimize interference.
- Consider using frequency coordination tools to find clear channels.
Low Signal Strength:
- Problem: Weak or inconsistent signal.
- Solution:
- Verify proper antenna positioning and orientation.
- Ensure there are no physical obstructions between the transmitter and receiver.
- Adjust the transmitter’s power output if possible.
Battery Problems:
- Problem: Unexpected power loss or erratic battery performance.
- Solution:
- Use fresh, high-quality batteries and replace them regularly.
- Check and clean battery contacts for a secure connection.
- Consider investing in rechargeable batteries for cost efficiency.
Frequency Congestion:
- Problem: Multiple wireless systems causing interference.
- Solution:
- Use a multi-channel receiver to accommodate various devices.
- Employ frequency scanning tools to identify open channels.
- Coordinate frequencies with other users if in a shared environment.

Audio Dropouts:
- Problem: Brief interruptions in audio transmission.
- Solution:
- Check for physical obstructions or interference sources.
- Verify the transmitter and receiver are within the recommended range.
- Inspect and replace cables if damaged.
Distorted Audio:
- Problem: Poor audio quality or distortion.
- Solution:
- Ensure the microphone element is clean and undamaged.
- Adjust transmitter gain levels to prevent clipping.
- Check for compatibility issues between microphone types and transmitters.
Encryption and Security:
- Problem: Concerns about unauthorized access or eavesdropping.
- Solution:
- Enable encryption features if available on your wireless system.
- Regularly update security settings and change passwords.
- Be aware of the regulatory requirements regarding wireless communication security.
Conclusion
In a world where wireless connectivity is increasingly prevalent, understanding the inner workings of wireless microphone systems is essential. This article serves as a comprehensive guide, unlocking the waves of technology that empower these systems and highlighting their significance in today’s audio landscape. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or an aspiring enthusiast, embracing the knowledge of how wireless microphone systems work is key to unleashing the full potential of audio creativity.





![Calgary’s Hottest Neighborhoods for Luxury Homebuyers [2024]](https://thewashingtonote.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/Calgary-324x160.png)



