Each of us at least once had to report on the work done. Some do it all the time, some do it occasionally, but anyway, if you want to get paid, prove that you worked hard. Why all this demagoguery? It’s easier to understand what PoW is. Before ordering blockchain development services at Peiko, it is worth understanding the basic concepts of the blockchain.
We have already written about one amazing property of the blockchain – decentralization. No third party is needed to confirm a transaction or deal. But a special algorithm is needed. Proof of Work or proof of work is the principle of protecting distributed systems from hacker attacks or spam. The main purpose of Proof of Work is to check the calculations made when creating a new block. Because the block calculation process is complex and random, it is impossible to accurately predict which of the miners will solve the problem and close the block. For a block to be considered true, its hash value must be less than the current target. Thus, each block shows that work has been done to find it.
In the first part, we wrote that all blocks have a hash of the previous block. You cannot change any block, but it is possible to create a new one. To achieve this, you need to find all the previous blocks. The high complexity of this process protects the blockchain from hacker attacks and unauthorized modifications.
For a simpler understanding, let’s give an example: a person performs complex and long work, then sends the results of this work to the system for verification. This system has a special “template of checks”, thanks to which the correctness of the solution is established in seconds. An important feature of this algorithm is the difference in time costs – a long request time and a fast response speed. We calculate something for a very long time, but we quickly check it.
But, in addition to the advantages, the algorithm also has disadvantages. The main disadvantage is the huge cost of computing power. Many prominent observers of crypto and blockchain technologies have compared PoW to a terrible monster that devours electricity day and night.
The alternative did not have to wait long. Many miners rejoiced when a new algorithm called Proof of Stake, or, in other words, proof of stake, appeared. And what matters here is not the power of your equipment, not the amount of time spent, but the balance of your wallet. This is the principle when money makes money: the more money you have in your wallet, the more profit you will make. To give examples, the PoW model is when you go to work and earn money (employee), and the PoS system is when you put your savings in a reliable bank and live on interest (rentier).
The degree of protection against attacks with PoS is much higher. Since to conduct an attack, you need to spend a lot of money. But if you buy 51% of the coins, then the market will react with a rapid price increase. Besides, what’s the point of attacking a network if most of the attacker’s resources are invested in virtual coins of the same network, and the attack will hit the sickest person – the wallet? If the attacker has many funds, and he produces it, then he himself will suffer from the attack, since this will violate the stability of the cryptocurrency. Cons of Proof of Stake, unfortunately, also exist.
Therefore, one of the geniuses of the blockchain community came up with the idea – to find a middle ground by combining the two algorithms Proof of Stake and Proof of Work.
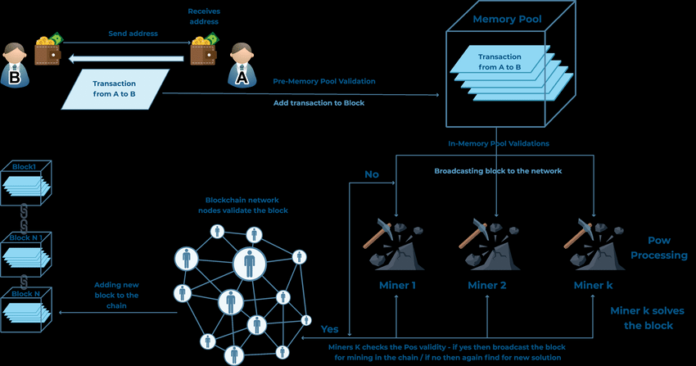
Hybrid PoW + PoS scheme
The resources spent on hashing blocks with the PoW algorithm are huge and far exceed the power of the largest supercomputers. In addition, PoW-cryptocurrency can be attacked by temporarily renting huge computing power.
PoS cryptocurrencies are potentially vulnerable to other types of attacks. For example, an attacker wanted to create a fork of the blockchain – a longer alternative chain by wasting “non-existent” resources. In addition, he can get the support of other miners because they also do not have to spend “genuine” resources.
Thanks to a fork, an attacker can block certain transactions and perform “double-spend” attacks. Such attacks can be divided into near and far. During close attacks, most of the last blocks are replaced, and at the time of long-range attacks, the attacker can replace the entire history of the network.
Under the standard hybrid scheme, the blockchain consists of two types of blocks. Both PoW and PoS blocks are searched at the same time. Proof of Work can be compared to a checkpoint, as PoW is mainly used to distribute new coins. Proof of stake is necessary to secure transactions, i.e., as the main means for generating blocks of transactions.
To successfully attack a project with a hybrid mechanism, the attacker must have 51% of the total computing power of the network and 51% of the total money supply. This creates two barriers of a different nature for the attacker, which protect the network from being compromised.

Advantages of PoW and PoS
Proof of Work and Proof of Stake are two different types of algorithms used in blockchain technology.
The advantage of Proof of Work is that it is very difficult to fake transactions on a blockchain. For example, if someone wanted to create a fake bitcoin transaction, they would have to solve the proof-of-work problem first. This makes it very difficult for anyone to cheat the system.
The idea of Proof of Stake is that instead of solving a proof-of-work problem, nodes in a blockchain network can “stake” their coins in order to participate in the network. The advantage of Proof of Stake is that it is less energy-intensive than Proof of Work. Additionally, nodes in a Proof of Stake network do not need to mine new coins; they simply need to hold a certain number of coins in order to participate. This makes it much easier for nodes to stay active in the network since they do not need to devote significant amounts of resources to mining.









